Bitcoin Miners Rake In $1.66B in August
In August, bitcoin miners generated revenues close to 1.65 billion dollars, a level almost identical to that of July. This maintenance reflects an impressive resilience of the sector, despite a context marked by rising costs and energy pressure. But behind this apparent stability lie structural vulnerabilities that raise questions: can the current mining model really hold in the long term?

In Brief
- Bitcoin miners generated between 1.633 and 1.66 billion dollars in August.
- Transaction fees now account for nearly 2% of revenues, compared to less than 1% previously.
- The number of pending transactions ranges between 85,000 and 93,000, signaling increasing congestion.
- Profitability remains far from pre-April 2024 halving levels.
Bitcoin Miner Revenues Hold Steady in August
Since late June 2025, the Bitcoin network has experienced a gradual increase in activity. In August, bitcoin miners generated between 1.633 and 1.66 billion dollars , almost the same amount as in July.
This stability confirms the solidity of their revenues, despite an environment still marked by strong competition and high energy costs.
Figures compiled by Newhedge and The Block show that block subsidies remain the backbone of this profitability.
Transaction fees, although modest in absolute value, around 1.30 dollars per transfer on average, are gaining importance. They now represent nearly 1.9% of total rewards, compared to less than 1% a few months ago.
This progress reflects growing activity on the blockchain. The mempool, a gauge of network congestion, showed between 85,000 and 93,000 pending transactions at the end of August, a sign of persistent bottlenecking.
In the short term, this dynamic supports miners’ revenues. But it also highlights their strong dependence on the intensity of on-chain exchanges, which is itself closely linked to market cycles and speculative movements driving the Bitcoin ecosystem.
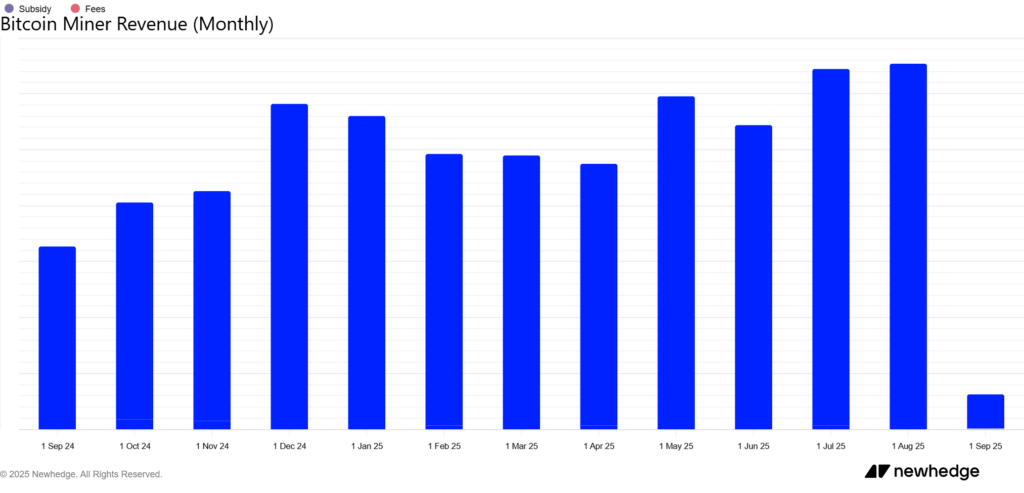 Monthly evolution of bitcoin miners’ revenues. Source: Newhedge.io.
Monthly evolution of bitcoin miners’ revenues. Source: Newhedge.io.
Between Resilience and Vulnerability, a Model Under Pressure
While August confirms the solidity of mining revenues, the sector remains under pressure. Margins remain 40 to 50% lower than the pre-halving period of April 2024. Network difficulty continues to rise.
This forces less competitive miners to seek solutions: energy optimization, pooling of hashrate , or relocation to low-cost areas.
In this context, bitcoin’s price, stabilized around 113,000 dollars, provides some support. However, it is not enough to offset the structural decline in profitability caused by the halving.
Miners thus find themselves in a paradoxical situation: their revenues appear stable on paper but remain fragile in the face of market uncertainties and energy costs.
The future of mining therefore rests on an essential triptych: the price of bitcoin , network difficulty, and the regulatory framework. As long as these three parameters remain uncertain, the sector’s profitability will remain under pressure.
In short, August thus illustrates the impressive resilience of miners , but also highlights a fundamental vulnerability: without a new upward impulse in bitcoin prices or major technological advances in energy, the sustainability of the mining model remains threatened.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Bitcoin, altcoins sell-off as Fed chair switch-up, AI bubble fears spook markets

From yen rate hikes to mining farms shutting down, why is bitcoin still falling?
The recent decline in bitcoin prices is primarily driven by expectations of a rate hike by the Bank of Japan, uncertainty regarding the US Federal Reserve's rate cut trajectory, and systemic de-risking by market participants. Japan's potential rate hike may trigger the unwinding of global arbitrage trades, leading to a sell-off in risk assets. At the same time, increased uncertainty over US rate cuts has intensified market volatility. In addition, selling by long-term holders, miners, and market makers has further amplified the price drop. Summary generated by Mars AI This summary was generated by the Mars AI model, and the accuracy and completeness of its content are still being iteratively updated.

The Economist: The Real Threat of Cryptocurrency to Traditional Banks
The crypto industry is replacing Wall Street's privileged status within the American right-wing camp.

Grayscale's Top 10 Crypto Predictions: Key Trends for 2026 You Can't Miss
The market is transitioning from an emotion-driven cycle of speculation to a phase of structural differentiation driven by regulatory channels, long-term capital, and fundamental-based pricing.

